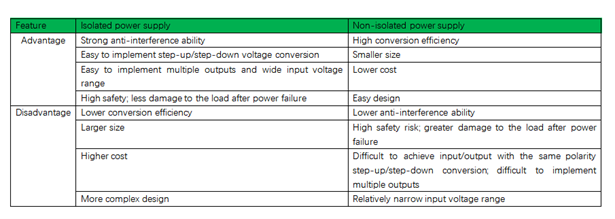
The difference between isolated and non-isolated power supplies
The difference between isolated and non-isolated power supplies
LEDs now is important in the lighting market. Their high brightness, low power consumption, long life, fast start-up, low power, no stroboscopic, and less prone to visual fatigue make them an important factor for consumers. In the LED driver industry, isolation and non-isolation are probably the two most commonly heard terms. So what are they?How can we distinguish them fastly?
Bottom side circuit
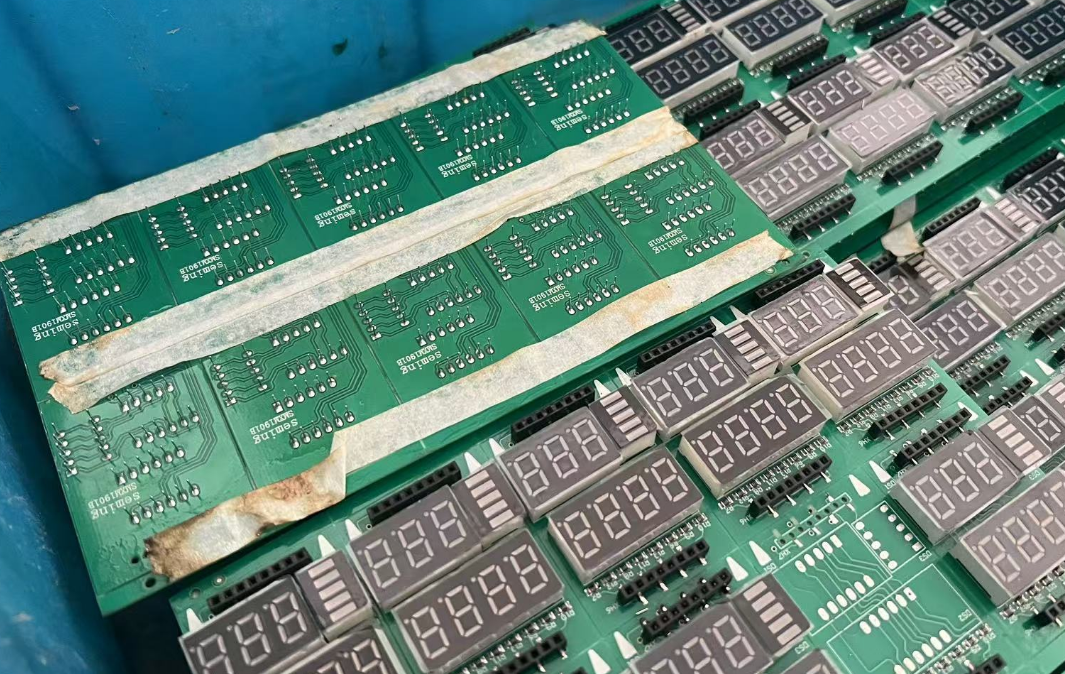
You can distinguish isolated and non-isolated by seeing the bottom side circuit at a glance! For isolated led drivers,there is no circuit below transformers on the bottom side, because the input side and output side is isolated. You can check following pictures.

What are the differences between them?
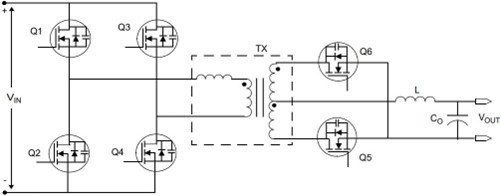
lsolation
lsolation in terms of DC/DC converters refers to galvanic isolation which means that there is no metallic / direct conduction path between two parts of the circuit. The isolation will always present a barrier between the input stage and the output stage and may be required for circuit functionality, safety, or both.The conversion process of the transformer is: electric-magnetic-electric, not connected to the earth, so there is no danger of electric shock.
Why Use an Isolated Power Supply?
Isolated power supplies are a key part of controlling the transfer of high amounts of energy and creating electronics safe for human contact. You might use an isolated power supply for:
Simplifying design and use: Many devices, like computers and TVs, have sensitive components that benefit from a more controlled energy flow. While they require more components, isolated power supplies can help designers and engineers easily meet these demands for controlled currents. They can also simplify use for the final product by eliminating special training requirements.
Meeting safety regulations and standards: Government and industry organizations — such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and Underwriters Laboratories (UL) — often require isolation for certain products. These regulations may outline certain types or grades of insulation depending on risk and product type.
Breaking ground loops: Ground loops form when two devices connect to both each other and the ground through different paths. They can disrupt the current flow and create noise or interference. Isolation can break up these loops and is often used for circuits that are sensitive to noise.
Creating a floating output: Floating outputs are ungrounded and do not reference another output. Many products use floating outputs to add safety. Others, like aircraft, need floating outputs because a ground connection is impossible. By connecting one terminal to another circuit node to fix it to that voltage, floating outputs can also invert or shift the output along the circuit.
Non-isolated
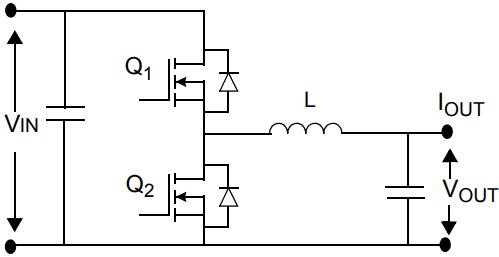
In general, non-isolated converters are less flexible in use than their isolated cousins.The primary difference is that a non-isolated converter does not have a transformer and does not require any physical separation between input and output, so this typically makes them smaller and lighter. It also improves the efficiency as there are no transformer losses to take into consideration.This reduction in BOM means that non-isolated converters tend to be lower in cost.The non-isolated circuit is directly added to the LED load after the input power is applied through the buck-boost, and there is a danger of electric shock.
Why Use a Non-Isolated Power Supply?
While they lack the safety features of an isolated power supply, non-isolated power supplies offer other benefits, like advantages in speed and design. When board-mounted near the load, they may be called point-of-load power supplies, which help reduce high incoming voltages to lower ones. Placing a non-isolated power supply downstream from an isolated power supply can help alleviate some safety concerns.
Since they don't require the additional components of an isolated supply, non-isolated units can offer:
More compact designs: Non-isolated systems don't need components like transformers and optocouplers, which allow designers to make smaller power supplies. They may be necessary when space is tight. Non-isolated power supplies also tend to offer higher switching frequencies, which can make some parts, like capacitors and magnetic components, smaller, further reducing the unit's size.
Cost savings: Without those extra components, a non-isolated power supply can be more affordable. A significant reason for the lower costs comes from swapping a transformer for an inductor. Transformers must often be custom-built, while inductors are easier to buy off the shelf. High levels of insulation can also increase the costs of an isolated power supply, which non-isolated units don't need.
More efficient operation: Non-isolated power supplies also have an efficiency advantage. The lack of isolation barriers provides direct control and monitoring of the output, which enables better performance and regulation. Plus, since they're smaller, non-isolated power supplies can sit closer to the load, which helps minimize adverse effects on the transmission line.
Summary
Isolation is a very useful feature within power solutions as it is able to provide safe operation, reduce noise / ground loops and allow flexibility in how the voltage rails are configured with respect to one another.
However, where non-isolated converters are able to be used, designers are able to take advantage of smaller size, higher power density, better efficiency and lower costs.
LEDs now is important in the lighting market. Their high brightness, low power consumption, long life, fast start-up, low power, no stroboscopic, and less prone to visual fatigue make them an important factor for consumers. In the LED driver industry, isolation and non-isolation are probably the two most commonly heard terms. So what are they?How can we distinguish them fastly?
Bottom side circuit
You can distinguish isolated and non-isolated by seeing the bottom side circuit at a glance! For isolated led drivers,there is no circuit below transformers on the bottom side, because the input side and output side is isolated. You can check following pictures.


lsolation in terms of DC/DC converters refers to galvanic isolation which means that there is no metallic / direct conduction path between two parts of the circuit. The isolation will always present a barrier between the input stage and the output stage and may be required for circuit functionality, safety, or both.The conversion process of the transformer is: electric-magnetic-electric, not connected to the earth, so there is no danger of electric shock.

Isolated power supplies are a key part of controlling the transfer of high amounts of energy and creating electronics safe for human contact. You might use an isolated power supply for:
Simplifying design and use: Many devices, like computers and TVs, have sensitive components that benefit from a more controlled energy flow. While they require more components, isolated power supplies can help designers and engineers easily meet these demands for controlled currents. They can also simplify use for the final product by eliminating special training requirements.
Meeting safety regulations and standards: Government and industry organizations — such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and Underwriters Laboratories (UL) — often require isolation for certain products. These regulations may outline certain types or grades of insulation depending on risk and product type.
Breaking ground loops: Ground loops form when two devices connect to both each other and the ground through different paths. They can disrupt the current flow and create noise or interference. Isolation can break up these loops and is often used for circuits that are sensitive to noise.
Creating a floating output: Floating outputs are ungrounded and do not reference another output. Many products use floating outputs to add safety. Others, like aircraft, need floating outputs because a ground connection is impossible. By connecting one terminal to another circuit node to fix it to that voltage, floating outputs can also invert or shift the output along the circuit.
Non-isolated
In general, non-isolated converters are less flexible in use than their isolated cousins.The primary difference is that a non-isolated converter does not have a transformer and does not require any physical separation between input and output, so this typically makes them smaller and lighter. It also improves the efficiency as there are no transformer losses to take into consideration.This reduction in BOM means that non-isolated converters tend to be lower in cost.The non-isolated circuit is directly added to the LED load after the input power is applied through the buck-boost, and there is a danger of electric shock.

While they lack the safety features of an isolated power supply, non-isolated power supplies offer other benefits, like advantages in speed and design. When board-mounted near the load, they may be called point-of-load power supplies, which help reduce high incoming voltages to lower ones. Placing a non-isolated power supply downstream from an isolated power supply can help alleviate some safety concerns.
Since they don't require the additional components of an isolated supply, non-isolated units can offer:
More compact designs: Non-isolated systems don't need components like transformers and optocouplers, which allow designers to make smaller power supplies. They may be necessary when space is tight. Non-isolated power supplies also tend to offer higher switching frequencies, which can make some parts, like capacitors and magnetic components, smaller, further reducing the unit's size.
Cost savings: Without those extra components, a non-isolated power supply can be more affordable. A significant reason for the lower costs comes from swapping a transformer for an inductor. Transformers must often be custom-built, while inductors are easier to buy off the shelf. High levels of insulation can also increase the costs of an isolated power supply, which non-isolated units don't need.
More efficient operation: Non-isolated power supplies also have an efficiency advantage. The lack of isolation barriers provides direct control and monitoring of the output, which enables better performance and regulation. Plus, since they're smaller, non-isolated power supplies can sit closer to the load, which helps minimize adverse effects on the transmission line.
Summary
Isolation is a very useful feature within power solutions as it is able to provide safe operation, reduce noise / ground loops and allow flexibility in how the voltage rails are configured with respect to one another.
However, where non-isolated converters are able to be used, designers are able to take advantage of smaller size, higher power density, better efficiency and lower costs.
Related Posts
Copyright © 2023 Zhejiang Seming Electronic Co., Ltd.